Step into the fascinating realm of architecture, where history, creativity, and innovation converge to shape our built environment. From ancient wonders to modern marvels, this journey will unravel the secrets behind iconic structures and the minds that brought them to life.
Delve deeper into the elements, structures, and visionaries that define the world of architecture as we know it today.
History of Architecture
Architecture has evolved significantly throughout history, reflecting the cultural, social, and technological advancements of different civilizations. From the monumental structures of ancient civilizations to the sleek skyscrapers of the modern era, architectural styles have continuously changed and adapted.Key architectural movements such as Gothic, Renaissance, and Modernism have played a pivotal role in shaping the built environment.
The Gothic style, characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, emerged in the Middle Ages and was often used in the construction of grand cathedrals. The Renaissance period brought a revival of classical Roman and Greek architectural elements, focusing on symmetry, proportion, and harmony.
Modernism, on the other hand, embraced new materials and technologies, leading to the development of minimalist, functional designs that rejected ornamentation.When comparing ancient architectural wonders like the Pyramids of Egypt and the Parthenon in Greece, both showcase the incredible engineering skills and artistic achievements of their respective civilizations.
The Pyramids, built as tombs for pharaohs, demonstrate the mastery of stone construction and precise mathematical calculations. In contrast, the Parthenon, dedicated to the goddess Athena, exemplifies the classical Greek architectural principles of balance, harmony, and ideal proportions.These examples highlight the rich diversity and innovation found in the history of architecture, showcasing how different styles and structures have influenced and inspired generations of architects and designers.
Elements of Architecture
Architecture is a multidimensional art form that involves various elements working together to create a harmonious and functional structure. The fundamental elements of architecture include form, space, light, and materials, each playing a crucial role in shaping the design and aesthetics of a building.
Symmetry and Balance
Symmetry and balance are key principles in architectural design, helping to create a sense of harmony and visual stability. Symmetry involves creating a balanced composition by arranging elements evenly on either side of a central axis. Balance, on the other hand, refers to the distribution of visual weight in a design, ensuring that no part overpowers the others.
Texture, Color, and Scale
Architects use texture, color, and scale to enhance the visual appeal of a building and create a sensory experience for the occupants. Texture adds depth and tactile quality to surfaces, while color can evoke emotions and set the mood of a space.
Scale, in terms of size and proportion, helps establish the relationship between different elements within a building and with its surroundings.
Types of Architectural Structures
Architectural structures can be classified into various categories based on their purpose and design. Some of the common types include residential, commercial, religious, and civic buildings.
Residential Buildings
Residential buildings are designed for people to live in and include houses, apartments, and condominiums. They are built with a focus on comfort, functionality, and aesthetics to create a cozy living space for individuals and families.
Commercial Buildings
Commercial buildings are constructed for business or commercial activities such as offices, retail stores, and restaurants. These structures are designed to accommodate the specific needs of businesses while also considering factors like accessibility, visibility, and branding.
Religious Buildings
Religious buildings serve as places of worship and spiritual reflection for various faiths. Examples include churches, mosques, temples, and synagogues. These structures often feature intricate architectural details and symbolic elements that reflect the beliefs and values of the religious community.
Civic Buildings
Civic buildings are designed for public use and include government offices, libraries, museums, and community centers. These structures are intended to serve the needs of the community while also embodying the cultural and historical identity of the region.
Iconic Architectural Landmarks
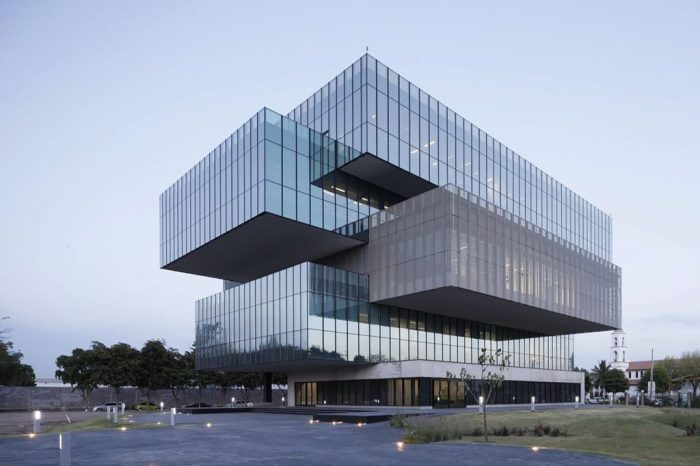

Some architectural landmarks have gained worldwide recognition for their unique design and cultural significance. Examples include the Eiffel Tower, Taj Mahal, and Sydney Opera House.
Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower in Paris, France, is known for its iconic iron lattice structure and towering height. Built in 1889, it has become a symbol of French engineering and architectural mastery, attracting millions of visitors each year.
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal in Agra, India, is a stunning white marble mausoleum built in the 17th century by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife. Its intricate carvings, domed architecture, and beautiful gardens make it a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a marvel of Mughal architecture.
Sydney Opera House
The Sydney Opera House in Australia is renowned for its sail-like design and striking waterfront location. Designed by Danish architect Jørn Utzon, this modern architectural masterpiece has become a symbol of Australia's cultural and artistic heritage.
Sustainable Architecture
Sustainable architecture focuses on creating buildings that minimize negative environmental impacts while maximizing energy efficiency and resource conservation. It aims to reduce carbon footprint, promote eco-friendly materials, and enhance indoor air quality.
Architects and their Works
Renowned architects play a crucial role in shaping the world of architecture with their unique styles and innovative designs. Let's delve into the works of iconic architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright, Zaha Hadid, and Le Corbusier, and explore the design philosophy behind some of their most famous projects.
Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright, known for his organic architecture style, believed in harmony between human habitation and the natural world. One of his most famous works is Fallingwater, a masterpiece that seamlessly integrates with its surroundings, featuring cantilevered balconies overlooking a waterfall.
Zaha Hadid
Zaha Hadid, a pioneer of parametric design, created futuristic and avant-garde structures that pushed the boundaries of architecture. The Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao is a prime example of her work, with its dynamic curves and unconventional form challenging traditional architectural norms.
Le Corbusier
Le Corbusier, a key figure in the modernist movement, focused on functionality and minimalism in his designs. Villa Savoye, a prime example of his work, showcases open floor plans, horizontal windows, and pilotis, reflecting his belief in the importance of space and light in architecture.
Architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Zaha Hadid, and Le Corbusier demonstrate how they balance functionality, aesthetics, and cultural influences in their designs, leaving a lasting impact on the world of architecture.
Closing Notes
As we conclude our exploration of architecture, we are left marveled by the intricate tapestry of history, design, and culture that defines this field. From the grandeur of past civilizations to the cutting-edge innovations of contemporary architects, the legacy of architecture continues to inspire and awe us.
FAQs
What are some key architectural movements throughout history?
Key architectural movements include Gothic, Renaissance, and Modernism, each influencing design in unique ways.
How do architects balance functionality and aesthetics in their designs?
Architects achieve balance by blending practical considerations with artistic elements to create harmonious spaces.
What is sustainable architecture and its impact on the environment?
Sustainable architecture focuses on eco-friendly design practices to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability.