Architectural works set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. From ancient civilizations to modern marvels, the evolution of architectural works unveils a tapestry of creativity, functionality, and cultural influences that shape our built environment.
Join us as we delve into the world of architectural wonders that have stood the test of time and continue to inspire awe and admiration.
Throughout history, architectural works have not only served practical purposes but have also been symbols of human ingenuity, artistic expression, and societal values. Let us embark on this fascinating journey together to explore the intricate blend of artistry and engineering that defines architectural works across the globe.
Introduction to Architectural Works
Architectural works encompass a wide range of structures such as buildings, houses, monuments, and other physical structures designed and constructed by architects. These works not only serve functional purposes but also reflect the culture, history, and creativity of a society.
Significance of Architectural Works
Architectural works play a vital role in society by shaping the built environment, providing spaces for living, working, and socializing, and contributing to the aesthetic appeal of a place. They also have the power to evoke emotions, inspire creativity, and influence the way we perceive our surroundings.
- Architectural works serve as landmarks and symbols of identity for cities and countries, such as the Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Sydney Opera House in Australia, and the Taj Mahal in India.
- They showcase the technological advancements and innovative design solutions of their time, like the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, and the High Line in New York City.
- Architectural works have historical significance, preserving the heritage and traditions of a place, such as the Acropolis in Athens, the Colosseum in Rome, and the Great Wall of China.
Historical Evolution of Architectural Works
Architecture has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations and has evolved significantly over time. From the monumental structures of ancient Egypt to the sleek skyscrapers of modern times, architectural works have undergone numerous transformations.
Ancient Architecture
Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans laid the foundation for architectural styles that are still influential today. Their use of grand columns, arches, and intricate detailing set the stage for future architectural developments.
Medieval and Renaissance Architecture
During the medieval period, Gothic architecture emerged with its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses. The Renaissance brought a revival of classical principles, focusing on symmetry, proportion, and harmony in design.
Modern Architecture
The 20th century saw the rise of modern architecture, characterized by innovative use of materials such as glass, steel, and concrete. Movements like Art Deco, Bauhaus, and Brutalism pushed the boundaries of design, leading to iconic structures around the world.
Sustainable Architecture
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable architecture, incorporating eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs. Concepts like green roofs, passive solar heating, and recycled materials are now common practices in architectural works.
Elements of Architectural Works
In architectural design, several key elements come together to create a cohesive and functional structure. These elements include form, function, aesthetics, space, light, and materials. Each plays a crucial role in shaping the overall design and experience of a building.
Form
Form in architecture refers to the shape and structure of a building. It includes the overall design, layout, and appearance of the structure. The form of a building can convey a sense of style, purpose, and identity, reflecting the architect's vision and the intended use of the space.
Function
Function is a fundamental element of architectural design, focusing on the practical purpose and usability of a building. Architects must carefully consider how the different spaces within a building will be used and how they can be optimized for efficiency and comfort.
The functionality of a building is essential for ensuring that it meets the needs of its occupants.
Aesthetics
Aesthetics play a significant role in architecture, influencing the visual appeal and emotional impact of a building. Aesthetic considerations encompass elements such as proportion, balance, harmony, and visual interest. Architects often use aesthetics to evoke specific feelings or create a particular atmosphere within a space.
Space, Light, and Materials
Space, light, and materials are critical components of architectural design that greatly influence the overall look and feel of a building. The manipulation of space helps define the functionality and flow of a building, while natural and artificial light can enhance the atmosphere and mood of a space.
Materials, such as wood, concrete, glass, and steel, contribute to the structure's durability, sustainability, and aesthetic qualities.
Integration with the Surrounding Environment
Architectural works are not isolated entities but are part of a larger ecosystem that includes the surrounding environment. Architects must consider how their designs interact with the natural and built environment, taking into account factors such as climate, topography, and local culture.
By integrating architectural works harmoniously with their surroundings, architects can create sustainable and contextually sensitive designs.
Architectural Design Process
The architectural design process involves a series of steps that architects follow to bring a project from concept to reality. It requires a balance of creativity and functionality, as well as the integration of technology and software to enhance the design process.
Concept Development
Concept development is the initial phase of the architectural design process where architects brainstorm ideas, create sketches, and develop a vision for the project. This stage is crucial in setting the tone and direction for the design.
Schematic Design
During the schematic design phase, architects start to translate the concept into more concrete plans. This includes creating rough drawings, floor plans, and elevations to visualize the layout and structure of the building.
Design Development
In the design development phase, architects refine the plans, consider materials, and make decisions on the technical aspects of the project. This stage involves a more detailed approach to the design process, focusing on the functionality and practicality of the building.
Construction Documents
The construction documents phase involves preparing detailed drawings, specifications, and documents that will guide the construction process. Architects work closely with engineers and contractors to ensure that the design is feasible and meets all necessary regulations.
Construction Administration
During the construction administration phase, architects oversee the building process, address any issues that arise, and ensure that the design is implemented correctly. This phase requires strong project management skills and attention to detail.
Creativity vs Functionality
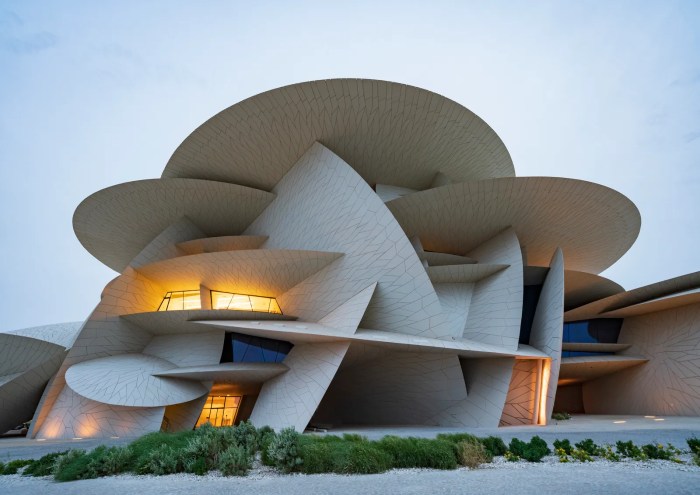

Architects must balance creativity with functionality in their designs to create spaces that are not only visually appealing but also practical and efficient. This involves finding innovative solutions to design challenges while considering the needs and requirements of the end users.
Use of Technology and Software
Modern architectural design heavily relies on technology and software to enhance the design process. Tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM) software allow architects to create detailed 3D models, simulate building performance, and collaborate with other professionals in real-time. The use of virtual reality and augmented reality also enables architects to visualize designs in a more immersive way, helping clients better understand the final outcome of the project.
Cultural Influences on Architectural Works
Culture, history, and societal values play a significant role in shaping architectural works. Architects draw inspiration from the traditions, beliefs, and customs of a particular culture to create buildings that resonate with the local community. Let's explore how cultural influences impact architectural designs and styles.
Regional and Historical Contrasts
When comparing architectural styles from different regions and time periods, it becomes evident how cultural influences have shaped the built environment. For example, the intricate carvings and vibrant colors of Indian temples reflect the spiritual beliefs of Hinduism, while the minimalistic design of Japanese tea houses highlights the importance of simplicity and harmony in Japanese culture.
Incorporating Cultural Elements
Architects often incorporate cultural elements into their designs to create meaningful spaces that resonate with the users. Whether through the use of traditional materials, symbolic motifs, or spatial arrangements, these cultural elements help establish a sense of identity and belonging within the built environment.
By blending modern techniques with traditional aesthetics, architects can create spaces that honor the past while embracing the future.
Sustainable Architecture
Sustainable architecture, also known as green architecture or eco-friendly architecture, is a design approach that focuses on creating buildings that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout their life cycle. This type of architecture aims to minimize the negative impact on the environment while enhancing the health and well-being of occupants.
Innovative Green Design Strategies
Green design strategies play a crucial role in sustainable architecture by incorporating various techniques to reduce energy consumption, waste generation, and overall environmental footprint. Some innovative strategies commonly used in sustainable architectural works include:
- Passive solar design: Utilizing the sun's energy for heating and cooling purposes through building orientation, shading, and natural ventilation.
- Green roofs and living walls: Installing vegetation on rooftops and vertical surfaces to improve air quality, reduce heat island effect, and manage stormwater runoff.
- Energy-efficient systems: Incorporating high-performance insulation, energy-efficient lighting, and renewable energy sources like solar panels to minimize energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Water conservation measures: Implementing water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling to reduce water usage and promote sustainable water management.
Impact on Environment and Communities
Sustainable architecture not only benefits the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, preserving natural resources, and promoting biodiversity but also creates healthier and more livable spaces for communities. By designing buildings that prioritize energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and sustainable materials, sustainable architecture contributes to the well-being of occupants and fosters a sense of environmental stewardship within communities.
End of Discussion
As we conclude our exploration of architectural works, we are reminded of the timeless legacy left by visionary architects whose creations have shaped landscapes and captured the essence of their eras. From the grandeur of ancient temples to the sleek lines of modern skyscrapers, architectural works continue to be a testament to human creativity and innovation.
Let us carry forward this appreciation for architectural marvels as we look towards the future of design and construction.
FAQ Summary
What defines architectural works?
Architectural works encompass the design, construction, and artistic expression of buildings and structures that serve both functional and aesthetic purposes.
How do architects balance creativity with functionality in their designs?
Architects achieve a balance between creativity and functionality by integrating innovative design concepts with practical considerations such as building codes, client needs, and sustainability requirements.
Why is sustainable architecture important?
Sustainable architecture is crucial in contemporary practice as it promotes environmentally friendly design solutions that minimize negative impacts on the planet and prioritize the well-being of communities.