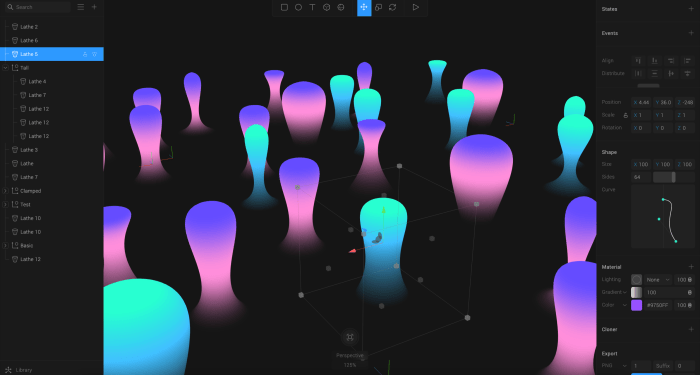
Spline design sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Exploring the intricate world of spline design reveals its vital role across various industries, showcasing its significance in product development and mechanical engineering.
Delving deeper into the realm of spline design unveils the different types of splines, the design process intricacies, and the manufacturing techniques that shape this fascinating field.
Overview of Spline Design
Spline design is a crucial concept in mechanical engineering and product development, involving the use of grooved or toothed shafts to transmit torque and rotational motion between components. These grooves or teeth, known as splines, provide a secure connection while allowing for relative motion between parts.
Significance of Spline Design
Spline design plays a vital role in various industries where precise transmission of power and motion is required. Some common applications of spline design include:
Automotive industry
Splines are used in the transmission systems of vehicles to transfer power from the engine to the wheels efficiently.
Aerospace industry
Splines are utilized in aircraft components for precise control of moving parts, such as flight control surfaces.
Industrial machinery
Splines are found in gearboxes, pumps, and other machinery for smooth and reliable power transmission.
Benefits of Spline Design
- Enhanced Power Transmission: Splines provide a strong and efficient method for transmitting torque, ensuring minimal power loss during operation.
- Improved Alignment: The use of splines allows for accurate alignment between mating components, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of the parts.
- Easy Assembly and Disassembly: Splined connections enable quick and easy assembly and disassembly of components, simplifying maintenance and repairs.
- Reduced Slippage: Splines prevent slippage between connected parts, ensuring reliable operation even under high loads or varying conditions.
Types of Splines
In spline design, there are several types of splines commonly used to transmit torque or motion between components. Each type has unique characteristics and applications that make them suitable for specific design requirements.
Involute Splines
Involute splines have a tooth profile that follows the involute curve, providing a smooth and gradual engagement. This type of spline is commonly used in gear connections and power transmission applications due to its ability to handle high torque loads efficiently.
Straight-Sided Splines
Straight-sided splines have a tooth profile with straight sides, unlike the involute spline. This type of spline is easier to manufacture and provides a more precise fit between components. Straight-sided splines are often used in applications where precise positioning and alignment are critical.
Serrated Splines
Serrated splines have teeth with a serrated or sawtooth-like profile, which allows for a higher load-carrying capacity compared to other spline types. This type of spline is commonly used in heavy-duty applications where shock loads and vibrations need to be absorbed.
Keyway Splines
Keyway splines have straight-sided slots (keyways) machined into the mating components, allowing for a simple and effective way to transmit torque. This type of spline is commonly used in shaft-hub connections where the torque requirements are moderate and precise alignment is needed.
Spline Design Process
Designing a spline involves a systematic process that ensures the final product meets the required specifications and functions effectively. From the initial concept to the final implementation, several steps need to be followed to create a successful spline design.
Considerations and Parameters in Spline Design
When designing a spline, several key considerations and parameters must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and durability. These factors play a crucial role in determining the overall effectiveness of the spline design.
- Load Capacity: The amount of load the spline will need to withstand during operation is a critical factor in determining the size and material of the spline.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right material for the spline is essential to ensure it can handle the required loads, resist wear, and maintain dimensional stability.
- Manufacturing Methods: The method used to manufacture the spline can impact its accuracy, strength, and overall quality. Factors such as machining processes, tolerances, and surface finish need to be considered.
Software Tools for Spline Design
Various software tools are commonly used by engineers and designers to aid in spline design and analysis. These tools help streamline the design process, optimize performance, and ensure accuracy in the final product.
- AutoCAD: A popular software for creating 2D and 3D spline designs, allowing for accurate modeling and analysis of spline components.
- ANSYS: Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software that can be used to simulate and analyze the performance of spline designs under different loading conditions.
- SolidWorks: CAD software that enables designers to create detailed spline models, perform stress analysis, and optimize spline geometry for performance.
Manufacturing Techniques for Splines
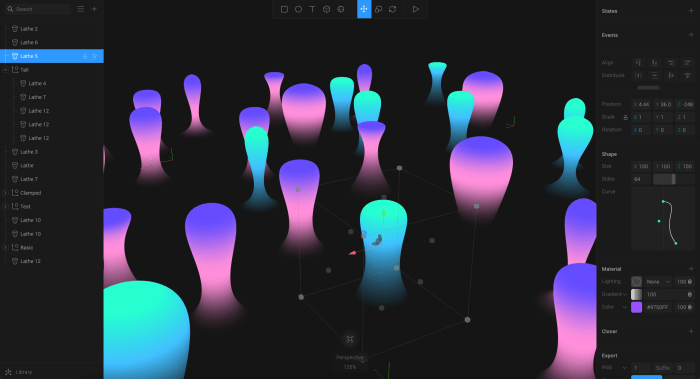
When it comes to manufacturing splines, there are several techniques that can be used to create these crucial components. Each method has its own set of advantages and limitations, and advancements in technology have further influenced the manufacturing processes involved.
Broaching
Broaching is a common method used to create splines, especially for high-volume production. This process involves a broach tool with multiple teeth that gradually increase in size, cutting the spline profile into the workpiece. One of the main advantages of broaching is its ability to produce accurate and consistent splines quickly.
However, broaching can be costly due to the specialized tooling required, making it more suitable for mass production rather than small-scale projects.
Hobbing
Hobbing is another popular method for manufacturing splines, particularly for gears and other cylindrical components. This process involves using a hobbing machine with a cutting tool called a hob to gradually create the spline profile on the workpiece. Hobbing is known for its high precision and efficiency, making it ideal for producing complex splines.
However, the initial investment in hobbing machines can be significant, making it more suitable for larger-scale production.
Shaping
Shaping is a versatile manufacturing technique that can be used to create splines with various profiles. This process involves a shaping machine with a cutting tool that moves in a reciprocating motion to shape the workpiece according to the desired spline profile.
Shaping is suitable for producing splines with low to medium production volumes and offers flexibility in terms of spline design. However, shaping can be slower compared to other methods like hobbing or broaching.Overall, advancements in technology have led to improvements in the manufacturing of splines, making processes more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective.
Manufacturers now have access to advanced CNC machines, software simulations, and cutting tools that enhance the production of splines, meeting the demands of modern industries for high-quality components.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the intricate dance between creativity and precision in spline design opens up a world of possibilities for innovation and efficiency. Navigating through the complexities and nuances of spline design leads to a deeper appreciation of its impact on modern engineering and product development.
Key Questions Answered
What are the different types of splines?
There are various types of splines used in design, such as involute splines, straight-sided splines, and serrated splines, each with unique characteristics and applications.
What software tools are commonly used for spline design and analysis?
Popular software tools for spline design include AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and ANSYS, which help in the intricate process of designing and analyzing splines.
How have advancements in technology influenced spline manufacturing?
Technological advancements have revolutionized spline manufacturing by enhancing precision, efficiency, and the overall quality of splines produced through methods like broaching, hobbing, and shaping.