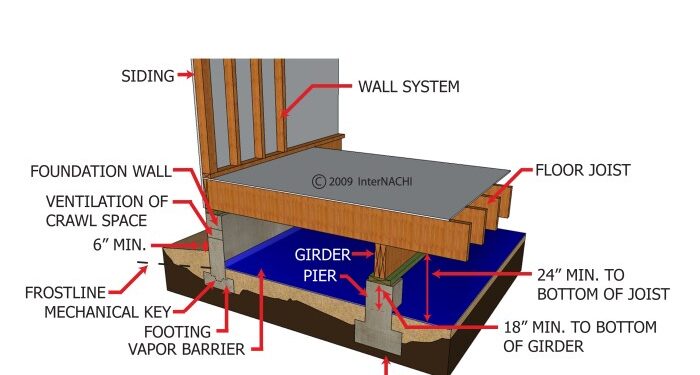
Delve into the world of crawl space siding as we explore the various materials, installation process, maintenance practices, and the importance of insulation and ventilation. This guide aims to provide a detailed insight for a well-rounded understanding of crawl space siding.
Types of Crawl Space Siding
When it comes to crawl space siding, there are various materials available to choose from. Each type comes with its own set of benefits and drawbacks, depending on factors like durability, cost, and maintenance requirements. Let's explore some of the common types of crawl space siding materials and their characteristics.
Vinyl Siding
Vinyl siding is a popular choice for crawl spaces due to its affordability, low maintenance, and wide range of colors and styles. It is durable and resistant to rot and insects, making it a long-lasting option for homeowners. However, vinyl siding can crack or fade over time, and it may not offer the same level of insulation as other materials.
Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is known for its durability and resistance to fire, insects, and rot. It can mimic the look of wood or stone siding without the same level of maintenance. While fiber cement siding is more expensive than vinyl, it offers better insulation and can last for many years with minimal upkeep.
Wood Siding
Wood siding provides a natural and classic look to crawl spaces, enhancing the overall aesthetic of a home. It is eco-friendly and can be painted or stained to match the homeowner's preferences. However, wood siding requires regular maintenance, such as painting or staining, to prevent rot, mold, and insect infestations.
Brick and Stone Veneer
Brick and stone veneer siding add a luxurious and timeless appeal to crawl spaces. They are durable, low maintenance, and provide excellent insulation. However, these materials can be costly to install initially, and repairs can be challenging and expensive if damaged.
Metal Siding
Metal siding, such as aluminum or steel, is highly durable, weather-resistant, and low maintenance. It can be painted or coated to prevent rust and corrosion, offering a modern and sleek look to crawl spaces. However, metal siding can be noisy during heavy rain or hailstorms, and it may dent or scratch easily.These are just a few examples of crawl space siding materials commonly used in residential and commercial projects.
Each type has its own unique characteristics and considerations, so it's essential to choose the right siding material based on your specific needs, budget, and aesthetic preferences.
Installation of Crawl Space Siding
Installing crawl space siding is a crucial step in protecting your home from moisture, pests, and other potential damage. It involves covering the exposed areas underneath your home to create a barrier against external elements.
Process of Installing Crawl Space Siding
- First, clean the crawl space area thoroughly to remove any debris or dirt that could interfere with the installation process.
- Measure the dimensions of the area to determine the amount of siding material needed for complete coverage.
- Securely attach the siding panels to the walls of the crawl space using appropriate fasteners, ensuring a tight and uniform fit.
- Seal any gaps or joints between the siding panels to prevent moisture infiltration and air leaks.
Tools and Equipment Required for Installation
- Hammer or nail gun for fastening the siding panels
- Tape measure for accurate measurements
- Caulk gun and sealant for sealing gaps
- Safety goggles and gloves for protection
- Ladder or scaffolding for reaching higher areas
Tips for Ensuring a Proper and Secure Installation
- Ensure that the siding material is appropriate for crawl space use and resistant to moisture and pests.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully for proper installation techniques.
- Inspect the siding regularly for any signs of damage or wear and tear, and make repairs as needed.
- Consider hiring a professional contractor for the installation if you are not confident in your DIY skills.
Maintenance of Crawl Space Siding
Proper maintenance of crawl space siding is essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the material. By following best practices and addressing common issues promptly, homeowners can prevent costly repairs and keep their crawl spaces in good condition
Common Issues with Crawl Space Siding
- Pest Infestation: Insects, rodents, and other pests can make their way into crawl spaces through damaged siding, causing structural damage and health hazards.
- Moisture Damage: Improperly installed or damaged siding can allow moisture to seep into the crawl space, leading to mold growth, rot, and deterioration of the structure.
- Physical Damage: Siding in crawl spaces is susceptible to physical damage from impacts, weather elements, and other external factors, compromising its integrity.
Provide solutions for addressing maintenance challenges effectively.
Effective Maintenance Solutions
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of the crawl space siding to identify any signs of damage, pest infestation, or moisture issues.
- Repair Damaged Areas: Promptly repair any damaged or deteriorating siding to prevent further issues and maintain the structural integrity of the crawl space.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the crawl space to prevent moisture buildup and reduce the risk of mold growth.
- Sealing Gaps: Seal any gaps or openings in the siding to prevent pests from entering and to maintain a secure barrier around the crawl space.
Insulation and Ventilation in Crawl Spaces
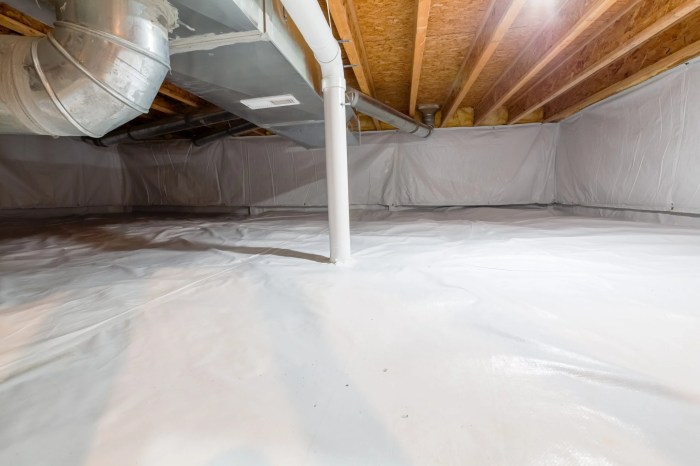

Insulation and ventilation play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and performance of crawl space siding. Proper insulation helps regulate temperature and moisture levels, while adequate ventilation ensures air circulation and prevents mold and mildew growth.
Importance of Insulation in Crawl Spaces
Insulation in crawl spaces helps to create a barrier between the interior of the home and the outside elements. It helps regulate temperature, reduces energy costs, and prevents moisture buildup. Without proper insulation, heat can escape in the winter and enter in the summer, leading to increased energy consumption and discomfort inside the home.
Impact of Ventilation on Crawl Space Siding
Ventilation in crawl spaces is essential to prevent moisture accumulation and maintain air quality. Proper ventilation helps to reduce humidity levels, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage. It also helps to remove stale air and odors, improving the overall indoor air quality of the home.
Optimizing Insulation and Ventilation
To optimize insulation and ventilation in crawl spaces, it is important to seal any gaps or cracks that may allow air and moisture to enter. Use insulation materials that are appropriate for crawl spaces, such as foam board or spray foam.
Additionally, ensure that vents are strategically placed to allow for proper air circulation without creating drafts. Regularly inspect and maintain both insulation and ventilation systems to ensure they are functioning effectively.
Ultimate Conclusion
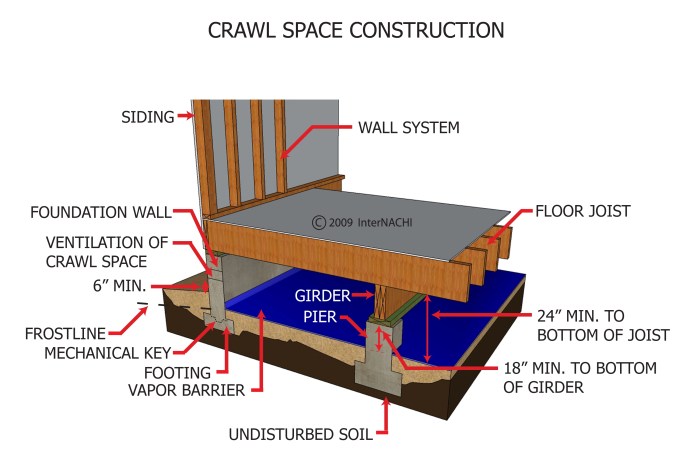
In conclusion, crawl space siding is a crucial aspect of any construction project, impacting both aesthetics and functionality. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you can ensure a durable and visually appealing solution for your crawl space.
Questions Often Asked
What are the common types of crawl space siding materials?
Common types include vinyl, wood, fiber cement, and metal.
What tools are needed for installing crawl space siding?
Tools like a circular saw, hammer, level, tape measure, and nail gun are commonly used.
How can I maintain crawl space siding effectively?
Regular cleaning, inspection for damage, and addressing any issues promptly can help maintain crawl space siding.
Why is insulation crucial in crawl spaces?
Insulation helps regulate temperature, reduce energy costs, and prevent moisture issues in crawl spaces.
How does ventilation impact crawl space siding performance?
Proper ventilation helps prevent moisture buildup, which can damage siding and lead to mold growth.